Arduino/DC Motors/PWM with transistor: Difference between revisions
Walttheboss (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Basics == == First Sketch == thumb We use a variable resistor to change the duty cycle. The motor is powered by any DC source. The midd...") |
Walttheboss (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Basics == | ==Basics== | ||
== First Sketch == | ==First Sketch== | ||
[[File:PWM with Transistor.jpg|thumb]] | [[File:PWM with Transistor.jpg|thumb]] | ||
We use a variable resistor to change the duty cycle. | We use a variable resistor to change the duty cycle. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
You power the motor from the positive side of the battery. | You power the motor from the positive side of the battery. | ||
The potentiometer simply | The potentiometer simply varies its resistance and the board translates that to a pwm value. | ||
<code>#define pwm 3 // Use pin 3 for the pwm output. | |||
#define pot A0 // the resistor will go on analog input pin 0 | |||
void setup() // put your setup code here, to run once: | |||
{ | |||
pinMode(pwm,OUTPUT); // Define pin pwm as an output. | |||
pinMode(pot,INPUT); // Define pin pot as an input. | |||
Serial.begin(9600); // Start the serial monitor. | |||
analogWrite(pwm,0); // Make sure the motor is off. | |||
} | |||
void loop() // This is the main code that runs till power off. | |||
{ | |||
float val = analogRead(pot); | |||
float duty = map(val,0,1023,0,255) // Change the input range of 1023 to the output range of 255 | |||
analogWrite(pwm,duty); // Set pin pwm to duty value. | |||
Serial.print("PWM = "); | |||
Serial.print(pwm); // Print the pwm value. | |||
Serial.print(" "); | |||
Serial.println(duty); // Print the Duty value and then do a carriage return. | |||
} | |||
</code> | |||
<br /> | |||
Latest revision as of 16:47, 14 May 2021
Basics
First Sketch
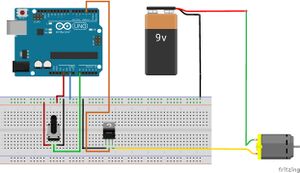
We use a variable resistor to change the duty cycle.
The motor is powered by any DC source.
The middle pin on the transistor is the control pin.
The left(flat/labeled/non-Heatsink) side is the ground.
The right pin is the voltage return to ground.
You power the motor from the positive side of the battery.
The potentiometer simply varies its resistance and the board translates that to a pwm value.
#define pwm 3 // Use pin 3 for the pwm output.
- define pot A0 // the resistor will go on analog input pin 0
void setup() // put your setup code here, to run once:
{
pinMode(pwm,OUTPUT); // Define pin pwm as an output.
pinMode(pot,INPUT); // Define pin pot as an input.
Serial.begin(9600); // Start the serial monitor.
analogWrite(pwm,0); // Make sure the motor is off.
}
void loop() // This is the main code that runs till power off.
{
float val = analogRead(pot);
float duty = map(val,0,1023,0,255) // Change the input range of 1023 to the output range of 255
analogWrite(pwm,duty); // Set pin pwm to duty value.
Serial.print("PWM = ");
Serial.print(pwm); // Print the pwm value.
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(duty); // Print the Duty value and then do a carriage return.
}