IT/Software/Backup Programs/Borg Backup: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
=== Pruning old backups === | ===Pruning old backups=== | ||
By default Borg will keep backups forever. | By default Borg will keep backups forever. | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
=== Backup Scripting === | ===Backup Scripting=== | ||
< | <code> | ||
#!/bin/bash | #!/bin/bash | ||
cd /location/to/be/backed/up | cd /location/to/be/backed/up | ||
borg create -C auto,lzma --progress /path/to/repo/::`date '+%Y-%m-%d-%H.%M.%S'` . | borg create -C auto,lzma --progress /path/to/repo/::`date '+%Y-%m-%d-%H.%M.%S'` . | ||
borg prune -v --list --keep-hourly=48 --keep-daily=30 --keep-monthly=12 /path/to/repo/ | borg prune -v --list --keep-hourly=48 --keep-daily=30 --keep-monthly=12 /path/to/repo/ | ||
</ | </code> | ||
Revision as of 20:13, 4 December 2020
About
Borg Backup is a backup program that features compression deduplication, data compression and runs nicely over SSH.
Usage
Repos
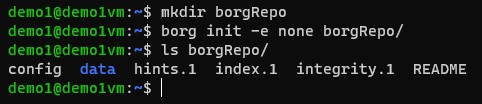
A Borg repo is where backup data is stored.
A repo can be created by running the following in an empty directory.
borg init -e none repoLocation
"-e none" is a required flag to tell bog that we don't want any encryption.
Creating a backup
When creating a backup we need to specify what kind of compression we want to use, where the repo we want to backup to is, and where the source files we want to backup are located.
borg create -C auto,lzma --progress repo/location/::name-of-backup location/to/be/backed/up
LZMA compression uses more CPU and less storage space.
Name of backup must be unique so using the date command instead of a static name is desirable when automating backups.
... repo/location/::`date '+%Y-%m-%d-%H.%M.%S'` location/to/be/backed/up
Backing up over SSH
In all Borg commands we can use ssh://ip.of.server/repo/location/on/server.
borg create -C auto,lzma --progress ssh://my.backup.server/repo/location/::name-of-backup location/to/be/backed/up
Viewing a repos backups
To list all the backups in a repo we can run the following:
borg list /path/to/repo
Restoring from a backup
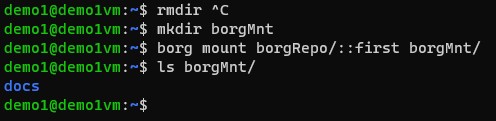
We can mount a Borg backup as if it was a regular drive anywhere in the filesystem.
borg mount /path/to/repo/::backupName mountPoint/
We can pull files from the backup as if it were a regular drive.
To unmount the backup we can run:
umount mountpoint/
Pruning old backups
By default Borg will keep backups forever.
We can prune backups by running borg prune.
borg prune -v --list --keep-hourly=48 --keep-daily=30 --keep-monthly=12 /path/to/repo/
In this example we will assume a backup job is running hourly.
In this example we will keep 1 backup per hour for the past 48 hours, 1 backup per day for the past 30 days, and 1 backup per month for the past 12 months.
Borg will keep the most recent backup from the time period it is pruning.
In the example we would keep the backup ran at 23:00 for the past 30 days and the last backup of the month for the monthly.
Backup Scripting
- !/bin/bash
cd /location/to/be/backed/up
borg create -C auto,lzma --progress /path/to/repo/::`date '+%Y-%m-%d-%H.%M.%S'` .
borg prune -v --list --keep-hourly=48 --keep-daily=30 --keep-monthly=12 /path/to/repo/